A MAP for FINDING YOUR WAY around MARS
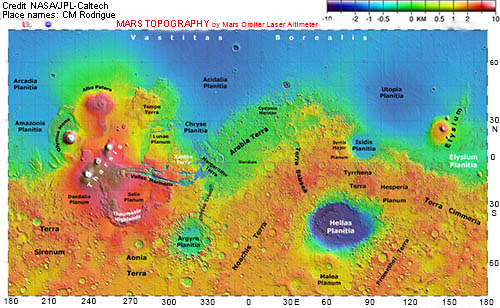
LONGITUDE in degrees E of zero reference point
Features of the Martian surface
- low plains called planitiae (singular: planitia)
- high plains and plateaus called plana (singular: planum)
- mountains and volcanoes called montes (singular: mons)
- canyons, chasms and valleys called valles (singular:vallis)
- rough cratered areas called terrae (singular: terra)
- dune fields (undae) shaped by the action of wind
- ice caps at N and S poles containing water ice and dry ice
- dust storms that can envelope the entire planet
- dark/light spots on global Mars; called albedo features
Map shows the surface of Mars colour-coded for altitude above or below the zero-elevation level - highest areas are white/red, lowest are blue.
Highest point: Olympus Mons, 21 km above zero-elevation level; lowest point: Impact crater in Hellas Planitia, 8 km below zero-elevation level.
A GALLERY of MARTIAN FEATURES



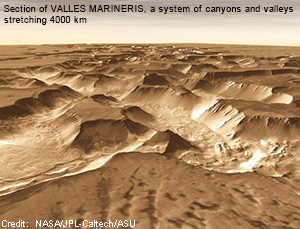


Information from orbiters and rovers over decades has revealed details of the surface of Mars. NASA/JPL has built this data into an interactive
program with many features, including locating surface features by name and measuring distances and altitudes.
